What Is Hypervigilance?
In the field of psychology, the term hypervigilance refers to excessively attentive monitoring or surveillance of one’s environment or inner world. This term is used to describe a psychological state or a specific behavioral trait. Here are some important characteristics of hypervigilance in psychology:
Hypervigilance:
People with hypervigilance pay excessive attention to events or thoughts around them. They can notice even small details and pay excessive attention to these details.
Hypersensitivity:
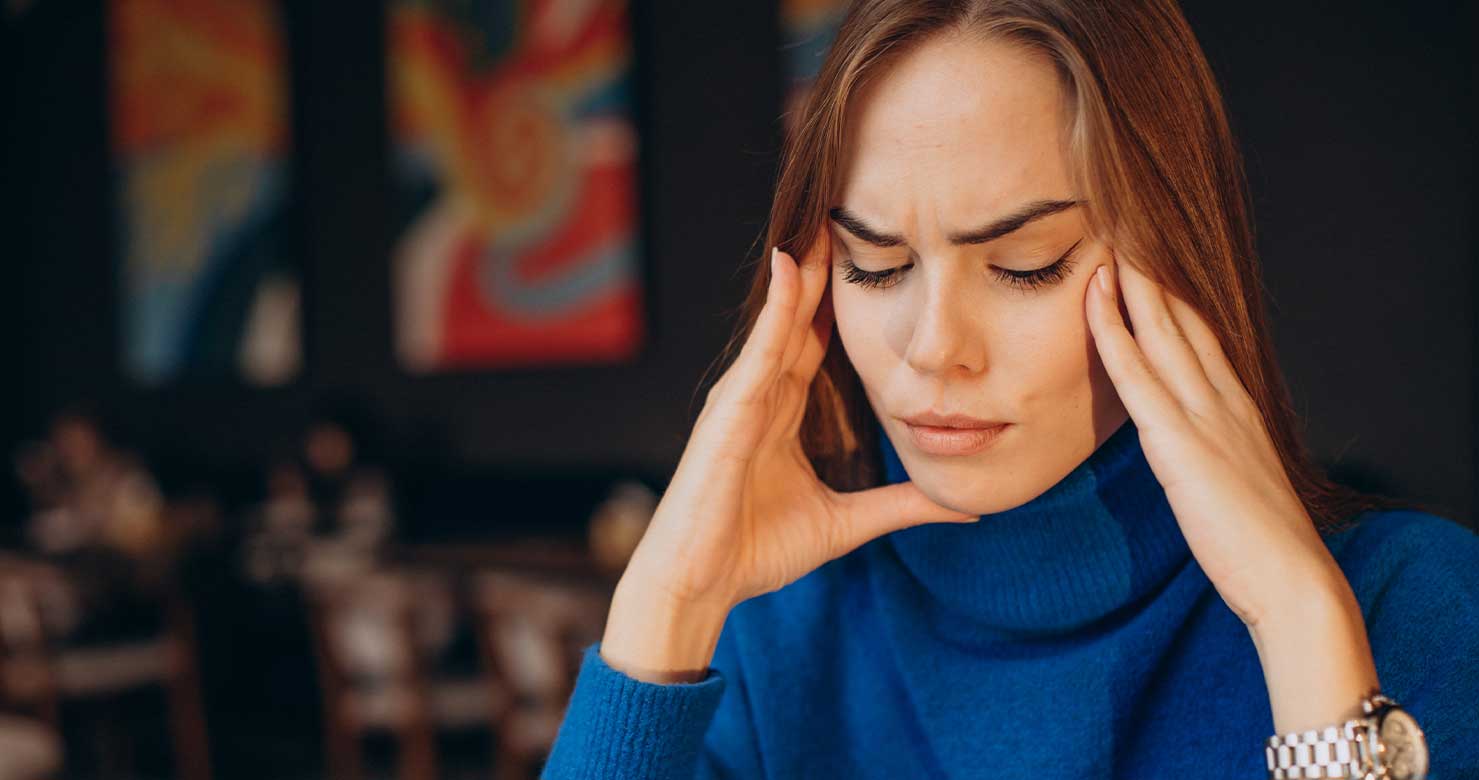
People with hypervigilance are quicker to perceive any potential threat or danger in their environment. This is often associated with conditions such as anxiety (anxiety disorder) or paranoia.
Thought Cycles:
Hypervigilance can be linked to situations where a person tends to overthink or worry constantly. The person may enter a loop in their own mind, constantly thinking about possible dangers.
Social Isolation:
People with hypervigilance may limit their relationships with others. This may be due to feeling overly suspicious or distrustful of the people around them.
Psychological Disturbance:
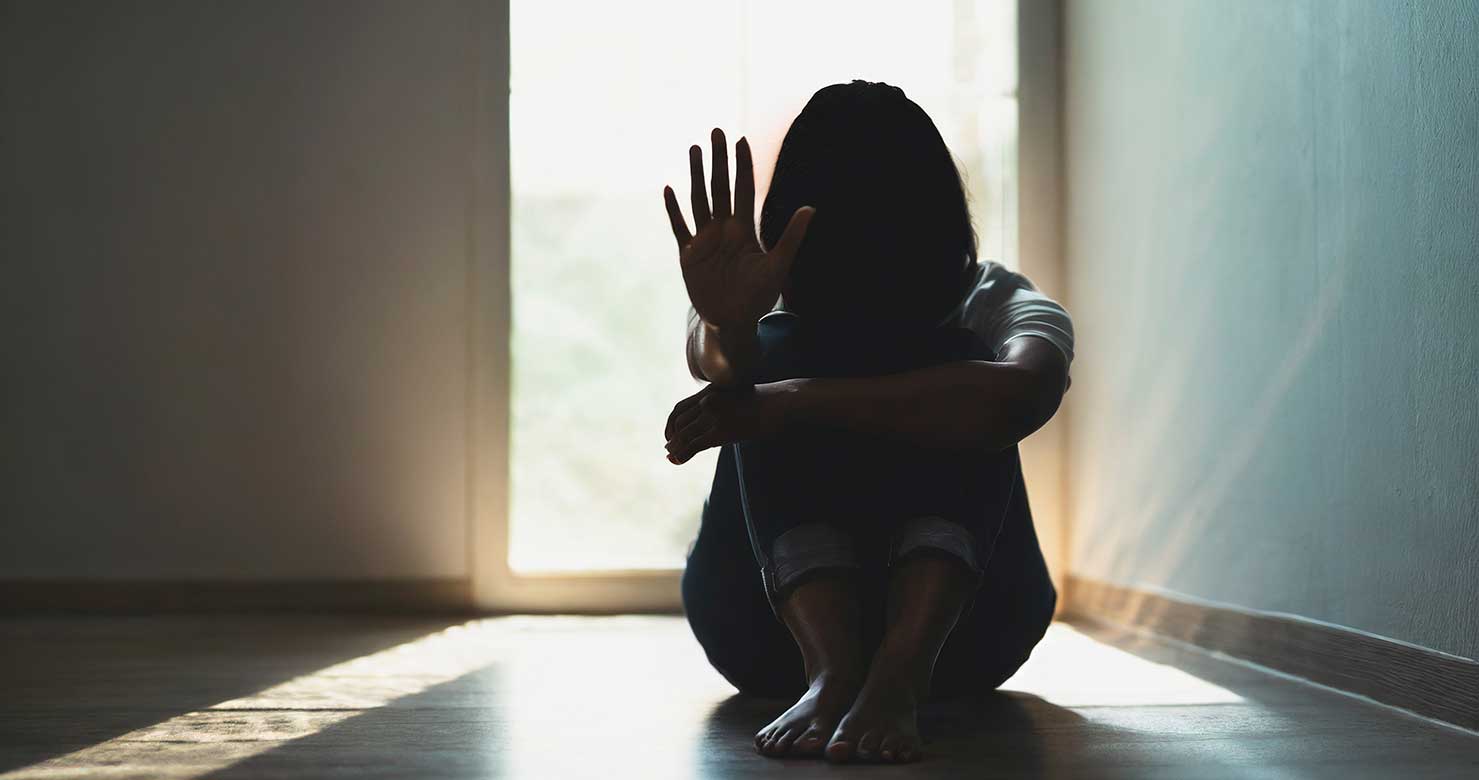
Hypervigilance can be a symptom of psychological disorders such as anxiety disorders. It can also develop as a result of a traumatic event.
In some cases, hypervigilance can function as a protective mechanism. For example, a person living in a dangerous environment can better detect dangers by observing their surroundings with extreme vigilance. However, when this becomes constant and excessive, it can reduce the quality of life and lead to psychological disorders. It is therefore important to consult a psychologist or psychiatrist to assess the origin and effects of hypervigilance.